AMD has disclosed that there is a high-severity vulnerability in the Ryzen Master software, which may potentially enable an adversary to gain complete control of the affected machine. Access to changing voltages and clock rates in real time is one of the many features that AMD Ryzen Master gives that makes it possible to exercise fine-grained control over the system. Other capabilities include: The multiplier on each AMD Ryzen CPU is unlocked from the factory, allowing you to tailor the processor’s performance to your own preferences. In order to take advantage of this significant benefit, AMD offers the AMD Ryzen Master application. While AMD Ryzen Master has developed to support an ever-expanding range of CPU products and features, the user interface has also developed to accommodate this expansion, becoming ever more complicated in the process. Due to poor permission validation during installation, the AMD Ryzen Master application—which has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2022-27677—could make it possible for a locally authorised attacker to run arbitrary code on the system. An adversary may exploit this issue to execute arbitrary code on the system while having higher privileges if they used installation files that they had carefully designed.
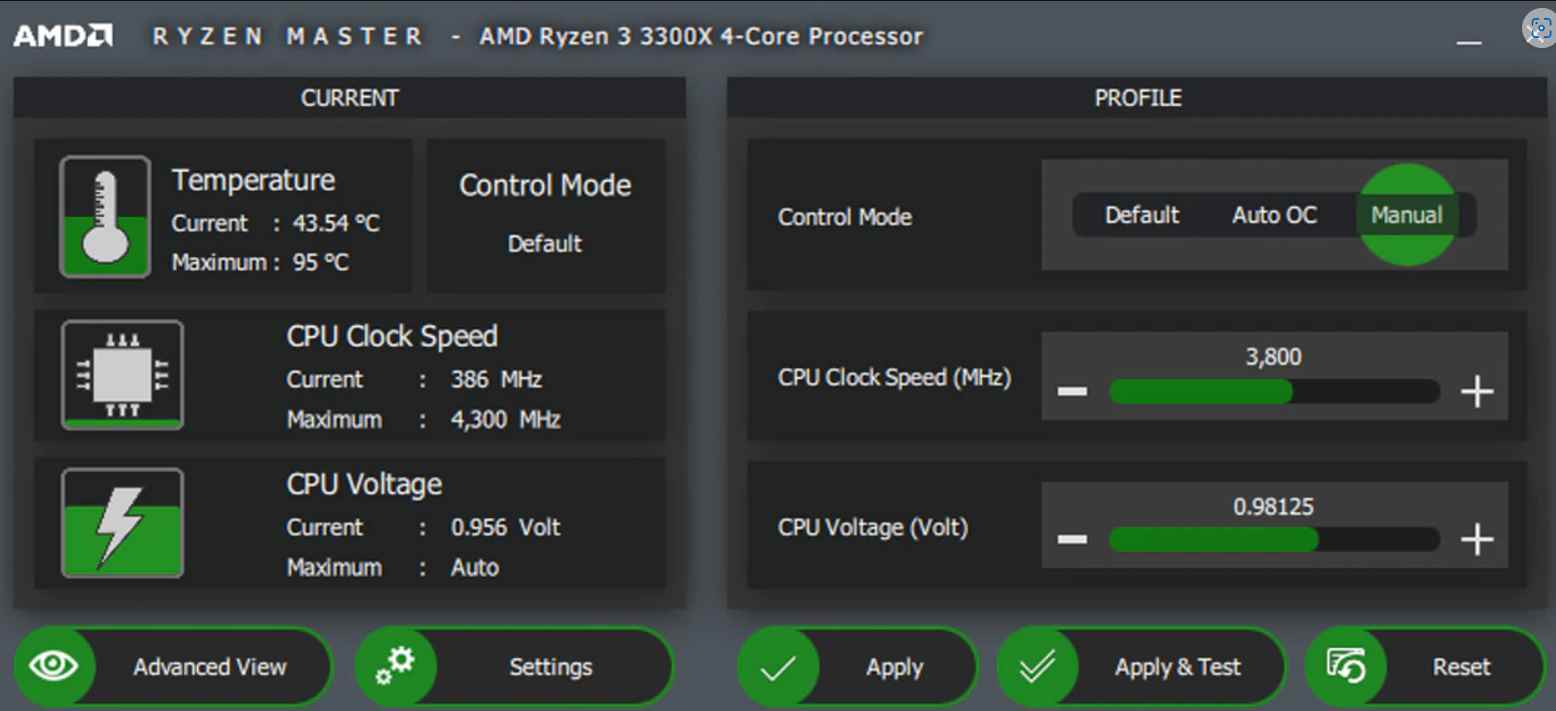
With a severity rating of 7.2 (High), this vulnerability might enable an adversary to take full control of the system. AMD notes that the problem stems from the fact that the privilege level of a user is not validated during the Ryzen Master installation process. This “may allow an attacker with low privileges to modify files,” which “may lead to privilege escalation and code execution by the lower privileged user,” according to AMD’s explanation of the problem.
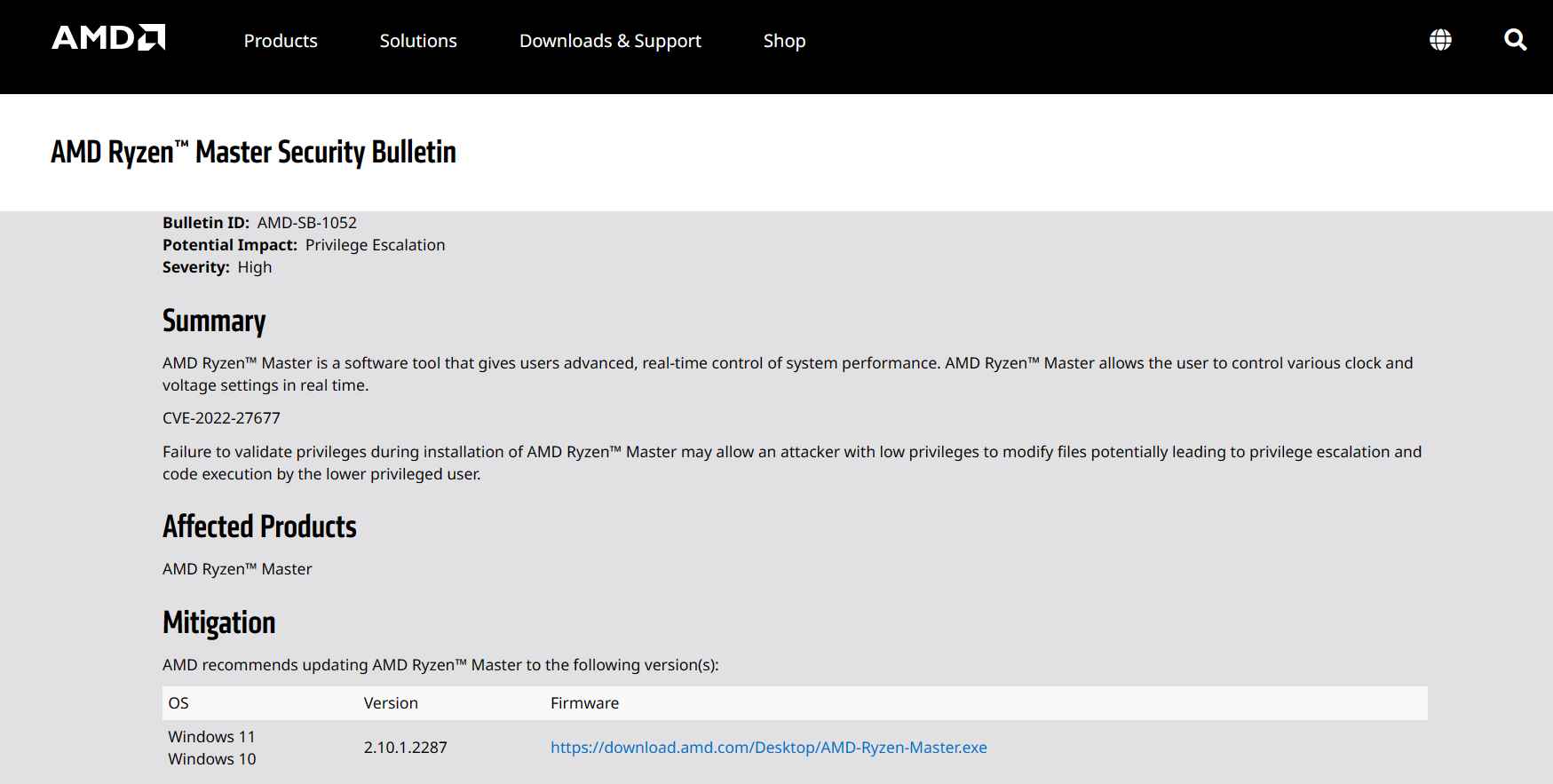
This indicates that a person with a low privilege level on a computer might utilize an earlier version of Ryzen Master to get administrator access, and eventually, complete control of the machine, by modifying significant files inside the operating system. Nevertheless, it is yet unknown if a person who does not have access to the administrator console may utilize the older installation program to aid an attack.
In order to address the CVE-2022-27677 vulnerability, AMD suggests that customers update their Ryzen Master software to the most recent version, which is version 2.10.1.2287. An earlier vulnerability in Ryzen Master that permitted privilege escalation that was found by HP in 2020(opens in new tab) has been fixed by AMD (CVE-2020-12928). The firm has only just fixed a mistake that enabled its graphics card drivers to automatically overclock the CPU without the user’s consent. Also, the company disclosed 31 newly identified security flaws a month ago.
In order to protect users from the security flaw and keep the software up to date, AMD suggests upgrading to at least the 2.10.1.2287 version. The new version has a few additional noticeable enhancements over the older version, one of which is the addition of support for setting a maximum operating temperature. This would decelerate the processor once it reached a temperature that was allocated to it once it reached that degree. Moreover, Ryzen Master now enables you to assign a voltage that is greater than 5.2 volts, which is much higher than the standard working voltage (although you shouldn’t do this unless you are well familiar with what you are doing). It is understandable that the vast majority of users will not need this functionality for the present chips; nonetheless, it is helpful for severe overclockers and may come in handy with future versions. Not all functionalities are supported by older CPUs, which is something to take note of.
Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.
