My Cloud from Western Digital is one of the most popular network-attached storage (NAS) devices that are being used by businesses and individuals to host their files, in addition to backing them up and syncing them with a variety of cloud- and web-based services. It is also one of the most widely used network-attached storage (NAS) devices. On unpatched My Cloud OS 5 devices, Western Digital has corrected a vulnerability that was of critical severity and might have allowed attackers to gain remote code execution and a reverse shell. This vulnerability, which has been assigned the identifier CVE-2022-29841, was brought about by a command that produced a system command without first cleaning the read data and then read files from a privileged location.

It is possible for remote threat actors to exploit this vulnerability in order to launch attacks against My Cloud devices that are running vulnerable firmware versions.
“A command that read files from a privileged location and created a system command without sanitizing the read data was the root cause of a remote code execution vulnerability, which has already been fixed. According to the business that specializes in data storage, “this instruction might be triggered remotely by an attacker in order to cause code execution and get a reverse shell.”
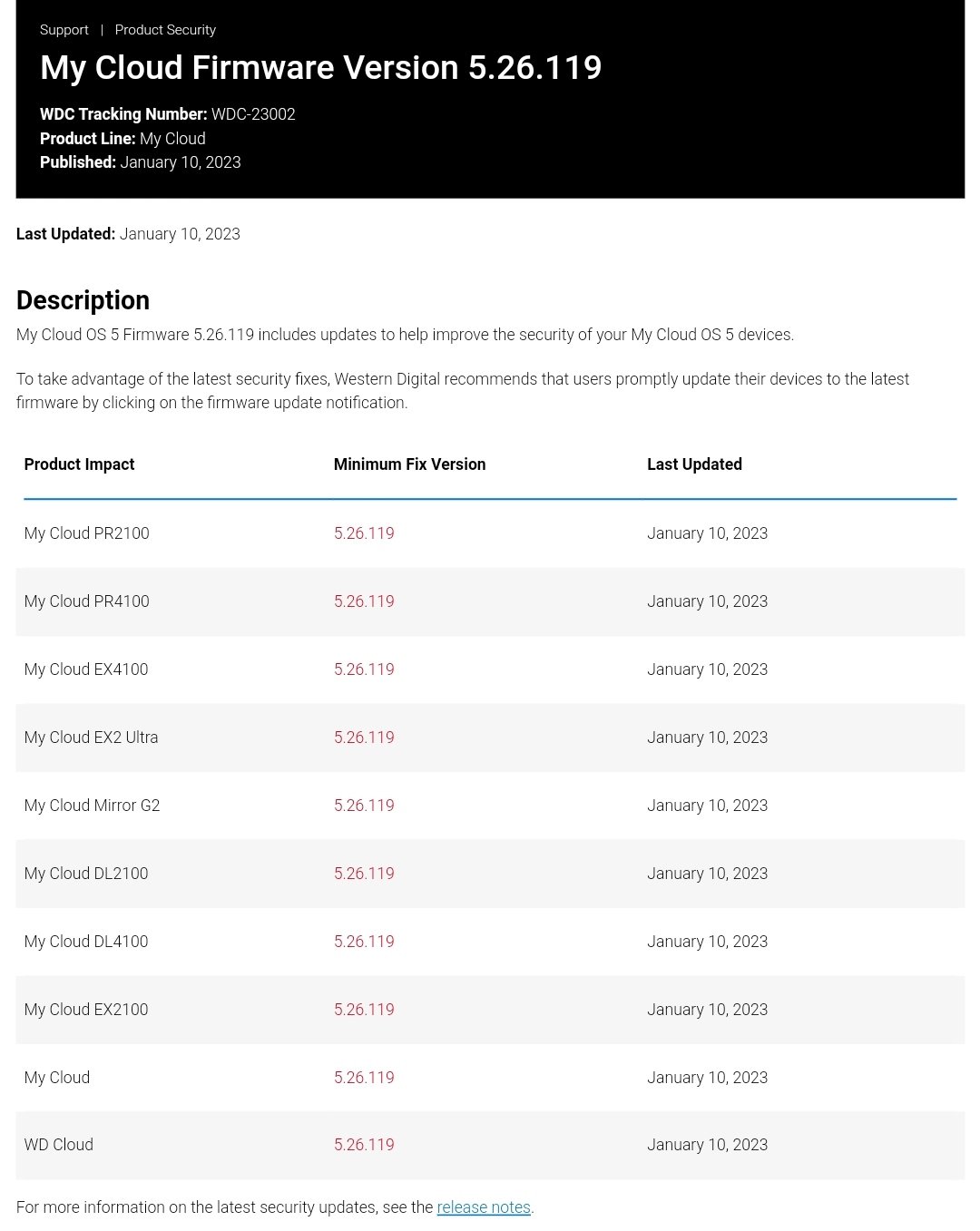
The following products are included on the list of susceptible devices according to the CVE-2022-29841 advisory:
In the My Cloud OS 5, Western Digital patched three additional vulnerabilities, which are as follows:
- My Cloud PR2100
- My Cloud PR4100
- My Cloud EX4100
- My Cloud EX2 Ultra
- My Cloud Mirror G2
- My Cloud DL2100
- My Cloud DL4100
- My Cloud EX2100
- My Cloud
- WD Cloud
CVE-2022-29842 is a fix for a command injection vulnerability that, if exploited, might let an attacker run code on a vulnerable CGI file in the context of the root user.
CVE-2022-29843 is a patch that addresses a vulnerability in the configuration of the DDNS service that had a CVSS score of 6.2. This vulnerability could have enabled an attacker to run code in the context of the root user.
CVE-2022-29844 is a memory corruption vulnerability in the FTP service that was fixed. This vulnerability could allow an attacker to read and write arbitrary files. The CVSS score for this vulnerability is 6.7. This might result in the complete compromise of the NAS, which would allow the attacker the ability to execute commands remotely.
Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.
