Due to the ongoing crisis all over the world , bad actors are constantly updating their phishing techniques to take the advantage of the scenario . Over the past three months, spammers everywhere are using the pandemic to spread phishing, scams and malware. Considering banks as a biggest source to fulfill their needs , this time the bad actors have seen to launch their campaigns in this sector . Researchers from MalwareHunterTeam , PhishLabz , Fire eye and PhishLabz have identified some of these campaigns delivering malicious email contents and text messages to the customers . They come across a campaign named “COVID-19 relief” which they operate in the name of “COVID-19 payment” . Their main targets are the users businessman and corporate worker based in US , Canada and Australia . This screenshot displays a fraud email sent to the citizens of Canada saying that your payment was approved by Canada’s Prime Minister , Justin Trudeau, and they claim the recipient can receive a check for 2,500 Canadian dollars if they fill out a form . The form which this email redirects to is a phishing page to steal your credentials .
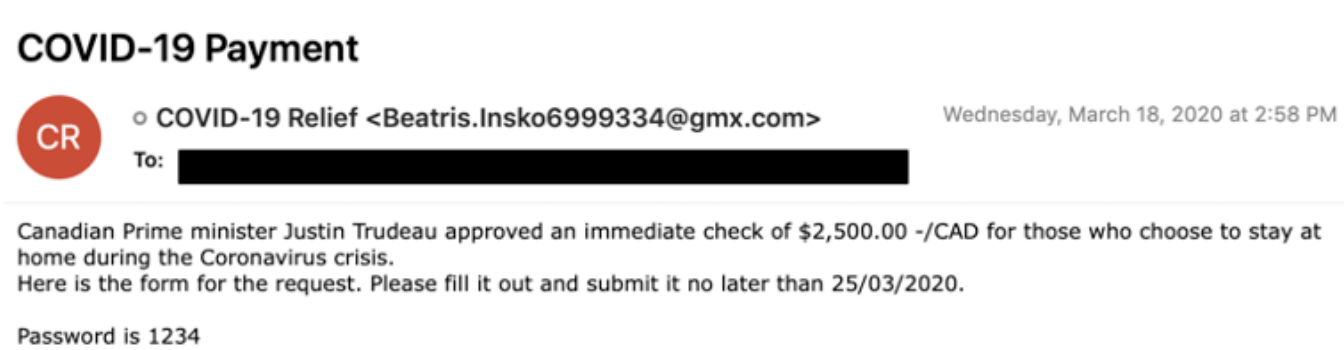
Another campaign carrying out in the name of Canadian bank is observed . The given link http://s4-update0{dot}.com/3/ in the screenshot redirects the user to a website asking for bank credentials .
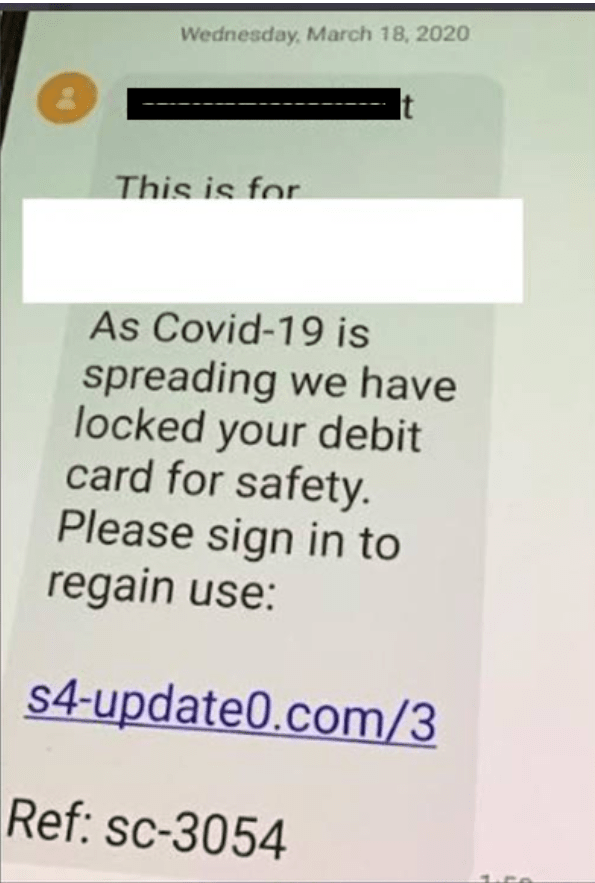
This screenshot is also an example of phishing targeting Canadian banks . By clicking the link, victims are led to emergencycanadaresponse.xyz and asked to choose their bank, as well as enter their account information.
But some hackers use some more brain and do social engineering to take the advantage in other way and lauched their trojan into the victim’ system. Coming back to Zeus Sphinix which almost made its presence in the market after three years , this trojan help the bad actors to do some fun with people in this crowdy season. In Sphinx’s case, the email tells victims that they need to fill out an attached form to receive monetary compensation for having to stay at home to help fight increasing infection rates . As soon as , the doc reaches to the end user , it asks the user to enable some macro which obviously indicates some wrong injections to your system . As soon as you enable the malicious macros desired by the document , the illegitimate script behind the document will start its deployment in your system , often using legitimate, hijacked Windows processes that will fetch a malware downloader that will communicate with C&C to launch the relevant malware for your system . After the malware gets embedded in your system , it then calls on its C&C server to fetch relevant web injections when infected users land on a targeted page and uses them to modify the pages users are browsing to include social engineering content and trick them into divulging personal information and authentication codes.
Sphinx signs the malicious code using a digital certificate that validates it, making it easier for it to stay under the radar of common antivirus (AV) tools when injected to the browser processes. In the following example, that file is named “Byfehi.”
Similar attacks phishing scams has also been observed in which the bad actors are targeting with the phishing emails titled “Internal Guidance for Businesses Grant and loans in response to respond to COVID-19 ”. The files attached to these emails lead to a fake message from the US Small Business Administration, which takes victims to a phishing page designed to harvest Microsoft account credentials.
HOW TO PROTECT FROM THESE ATTACKS ?
Government authorities of various countries are continuously keeping their citizens updated with the news attacks but it is important for people not only to understand but also implement these points :
- Do not visit to any malicious or suspicious website that you might think is wrong .
- Always see the flags when you visit any URL i.e. do not enter any sensitive information to the flag set by your browser as “not secure“.
- Keep your list of validated users in your system updated . Remove unwater validators .
- If found any suspicious URL , use virus total or any other antivirus tool to check it .

RSU is security researcher who is constantly working to make world a secure place to live. He is working day and night in Cyber Security area.
