In an unprecedented development, major fishing gear company Angling Direct was the target of an unusual cyberattack that resulted in the redirection of its web domain to the popular adult content platform Pornhub. While this may seem funny, the store’s official platform remains out of order, generating bewilderment among its hundreds of customers in the UK.
As Threatpost points out, the threat actors would have gained access to the credentials of the store’s social media account, from where they published a fake news about Angling Direct being sold to MindGeek, the company that owns Pornhub, and even offering a supposed one-month Premium subscription to customers.
Shortly after posting this not-so-funny joke, threat actors posted a new tweet, confirming the cyberattack but not demanding a ransom in exchange for handing over control of the compromised platforms to their rightful owners.
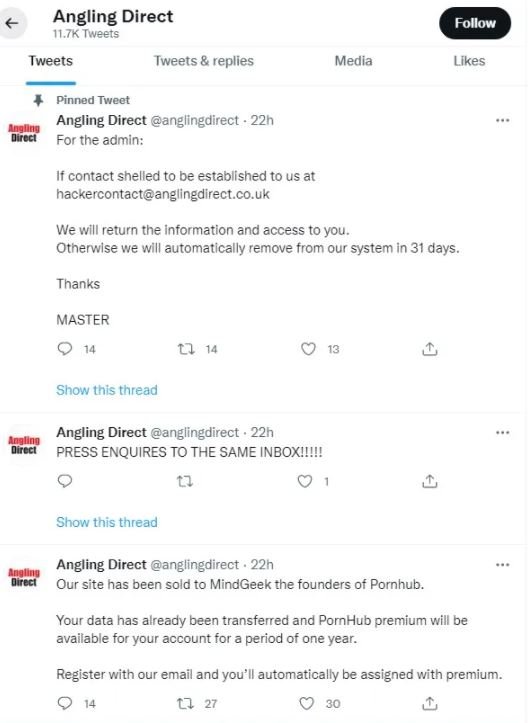
The hackers, identified as MASTER, only mention that control will be returned to Angling Direct within 31 days, although not much more is known about the matter. The company had to issue an official statement confirming the incident and pledging to conduct a detailed investigation.
On Tuesday afternoon, a spokesperson for Angling Direct confirmed that the company regained control of its social media platforms and the process of resetting the website was already nearing completion, so they hope to return to normal operations later this week. The representative concluded by mentioning that the relevant authorities and regulatory entities were notified about this incident.
About the attackers, any trace of activity simply disappeared after the company was able to regain control of its online platforms, so it is unknown if they are still active or if they received any payment in exchange for stopping their malicious activities. It is also unknown if there was a leak of confidential data resulting from this attack, although so far there is no evidence of it.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
